What is Google Ads?
Google Ads, formerly known as Google AdWords, is Google’s advertising system that allows businesses to display their ads on Google’s search engine and other Google properties. It’s an essential tool for businesses aiming to reach a wide audience, increase brand visibility, and drive traffic to their websites. With Google Ads, advertisers have the flexibility to set budgets, target specific audiences, and measure the success of their campaigns.
Google Ads is a powerful digital advertising platform that has become a cornerstone of marketing strategies for businesses of all sizes. In this comprehensive guide, we will discuss the world of Google Ads, shedding light on some of its most crucial metrics: Cost-Per-Click (CPC), Click-Through Rate (CTR), and Conversion Tracking.
Understanding these metrics is essential for advertisers looking to maximize the effectiveness of their campaigns and achieve a solid return on investment (ROI). These metrics are the foundation of any successful Google Ads campaign.
What is CPC?
At its core, Cost-Per-Click (CPC) is the price you pay every time a user clicks on your advertisement. Think of it as the toll booth fee for each visitor to your website via your ad. This straightforward definition conceals the complexity of how CPC is determined within the Google Ads ecosystem.
When you enter the world of Google Ads, you enter an intricate auction system. Advertisers compete for ad placement in Google’s search results, and the price they are willing to pay for a click is their bid. However, the highest bidder doesn’t always win. Google also considers the ad’s quality and relevance to ensure that users see ads that are genuinely valuable to them.
Factors Influencing CPC
Understanding CPC is not just about knowing what it is; it’s about grasping the myriad of factors that influence it. Here are the key influencers of CPC in Google Ads:
Keywords
Your choice of keywords has a significant impact on your CPC. Highly competitive keywords, often related to popular industries or products, can demand higher CPCs. Conversely, long-tail keywords, which are more specific and have less competition, typically offer more cost-effective CPC options.
Competition
The level of competition within your industry or niche plays a significant role in CPC. If many advertisers are vying for the same keywords, the bids naturally increase as they try to secure a position at the top of the search results.
Quality Score
Google assigns a Quality Score to each of your keywords based on factors like ad relevance, landing page quality, and expected click-through rate. A higher Quality Score can lead to lower CPC. It’s Google’s way of rewarding advertisers who create relevant, user-friendly ad experiences.
Understanding these factors is the first step in optimizing your CPC. You need to carefully strategize your keyword selection, monitor your competition, and work on improving your Quality Score.
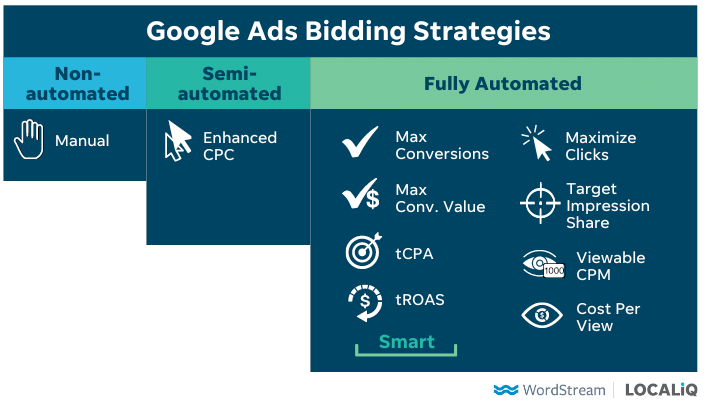
CPC Bidding Strategies
In Google Ads, you have several bidding strategies at your disposal, each designed to meet specific campaign objectives. Here’s a look at some common CPC bidding strategies and their pros and cons:
Manual CPC
With this strategy, you set your CPC bids manually. It provides you with complete control over your budget, allowing you to allocate specific amounts to different keywords or ad groups. This can be beneficial for advertisers who want fine-grained control.
Pros:
- Full control over bidding.
- Easy to adjust bids as needed.
Cons:
- Time-consuming to manage, especially for large campaigns.
- May not take full advantage of real-time data.
Enhanced CPC (eCPC)
Enhanced CPC is a semi-automated strategy that allows Google to adjust your manual bids based on the likelihood of conversion. It aims to get you more conversions while staying close to your specified CPC.
Pros:
- Utilizes machine learning to optimize bids.
- Can help maximize conversions within your budget.
Cons:
- Less control over individual keyword bids.
- May not work optimally for all campaign types.
Target CPA (Cost-Per-Acquisition)
With Target CPA bidding, you set a target cost for each acquisition or conversion. Google adjusts your CPC bids to achieve this target.
Pros:
- Focuses on acquiring customers at a specific cost.
- Uses historical data and machine learning for optimization.
Cons:
- Requires sufficient historical conversion data to be effective.
- May not work well if your target CPA is unrealistically low.
Choosing the right bidding strategy depends on your campaign goals, budget, and the level of control you want over your CPC bids. Experimenting with different strategies and monitoring their performance is often the best way to find the optimal approach for your specific situation.
Google Ads Average Cost Per Click
Google Ads, a dominant platform in the realm of online advertising, operates primarily on a pay-per-click (PPC) model, where advertisers pay a fee each time their ad is clicked. The Average Cost Per Click (CPC) is a vital metric that represents the average amount an advertiser pays for a single click on their ad.
This figure can vary greatly based on several factors, including the competitiveness of the keywords targeted, the quality of the ad and landing page, and the overall bidding strategy implemented. By understanding and optimizing the Average CPC, advertisers can better allocate their budget, maximize their return on investment, and strategically position themselves against competitors in the vast digital marketplace.
Click-Through Rate (CTR)
Measuring Ad Effectiveness
Let’s focus on a metric that holds a special place in the hearts of digital advertisers: Click-Through Rate (CTR). CTR is the litmus test for ad effectiveness, and in this chapter, we will explore what it is, why it matters, how it’s calculated, and strategies to boost it.
What is CTR?
Click-Through Rate (CTR) is the percentage of users who click on your ad after seeing it. In essence, it’s a measure of how effective your ad is at enticing users to take action. Understanding CTR is crucial because it reflects the relevance and appeal of your ad to your target audience.
Why CTR Matters:
- Effectiveness Gauge: CTR provides immediate feedback on how well your ad resonates with users. A high CTR indicates that your ad is compelling and engaging.
- Quality Score: CTR is one of the components Google uses to calculate your Quality Score, which directly impacts your ad’s position and CPC.
- Budget Efficiency: A higher CTR can lead to a lower Cost-Per-Click (CPC), ensuring that you get more clicks for the same budget.
How CTR is Calculated
The formula for calculating CTR is relatively straightforward:
- CTR = (Total Clicks / Total Impressions) x 100
- Total Clicks: The number of times users clicked on your ad.
- Total Impressions: The number of times your ad was displayed to users.
For example, if your ad received 500 clicks and was shown 10,000 times, your CTR would be calculated as follows:
- CTR = (500 / 10,000) x 100 = 5%
- This means that 5% of users who saw your ad clicked on it.
Improving CTR
Boosting CTR is a top priority for advertisers, as it can lead to better ad placement and more efficient use of your advertising budget. Here are some strategies to help you improve your CTR:
- Crafting Compelling Ad Copy: Your ad’s text is often the first interaction users have with your brand. Craft enticing headlines and descriptions that speak directly to your target audience’s needs, desires, and pain points. Use compelling language and clear calls to action to encourage clicks.
- Utilizing Ad Extensions: Ad extensions provide additional information and features alongside your ad. They not only make your ad more informative but also increase its visual prominence. Extensions like site links, callouts, and structured snippets can give users more reasons to click on your ad.
- A/B Testing: Continuous testing is crucial for improving CTR. Create multiple ad variations and test them against each other to identify which elements resonate best with your audience. This can include testing different headlines, descriptions, and even visual elements.
- Ad Relevance: Ensure that your ads are highly relevant to the keywords and search queries they’re targeting. Irrelevant ads are less likely to attract clicks and can negatively impact your Quality Score.
- Landing Page Experience: The quality of your landing page also affects CTR. Make sure your landing page provides a seamless and relevant user experience. Ensure that the content aligns with the ad’s promise and that the page loads quickly on both desktop and mobile devices.
- Negative Keywords: Use negative keywords to filter out irrelevant traffic. This can help improve CTR by ensuring that your ads are displayed to users who are more likely to be interested in your products or services.
What Kinds of Ads Have the Lowest CTR?
Research indicates that generic or overly broad ads often have the lowest CTRs. These lack a targeted message or fail to resonate with a specific audience. Additionally, ads that are poorly designed, have weak call-to-actions, or appear in non-relevant contexts can also suffer from low click-through rates. In the realm of display advertising, banner ads, especially those that employ repetitive or stale imagery, have historically witnessed declining CTRs. It’s essential for marketers to understand these nuances, refine their strategies, and create compelling, targeted content to improve their CTR.
Conversion Tracking & Measuring ROI
Conversion Tracking isn’t just another metric; it’s your compass for measuring Return on Investment (ROI) and understanding the actions users take after clicking on your ads. In this chapter, we’ll explore what Conversion Tracking is, how to set it up, and how to interpret the data it provides.
What is Conversion Tracking?
Conversion Tracking is the process of monitoring and measuring the actions users take on your website after clicking on your Google Ads. These actions, known as conversions, can vary widely depending on your campaign goals. Conversions may include purchases, sign-ups, form submissions, app downloads, or any other valuable interactions that align with your objectives.
Understanding conversions is critical because they go beyond click-through rates (CTR) and traffic numbers. Conversions represent real results, reflecting how your ads impact your business’s bottom line. They allow you to calculate your campaign’s ROI and make informed decisions to optimize your advertising strategy.
Setting Up Conversion Tracking
Setting up Conversion Tracking in Google Ads is a pivotal step in ensuring you can measure the success of your campaigns accurately. Below, we provide a step-by-step guide on how to set up and configure Conversion Tracking:
- Define Your Conversion Goals: Start by defining your conversion goals. What specific actions do you want users to take on your website? These could be making a purchase, filling out a contact form, subscribing to a newsletter, or any other meaningful action.
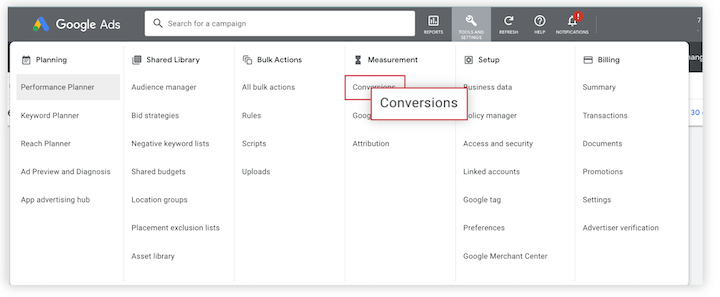
- Create Conversion Actions: In Google Ads, navigate to the Conversion section and create conversion actions based on your defined goals. You’ll need to specify the type of conversion you’re tracking and provide details like the conversion value, tracking method (e.g., website, app, or phone call), and attribution settings.
- Install the Conversion Tracking Code: Google Ads will generate a unique tracking code for each conversion action you create. This code needs to be placed on the relevant pages of your website or in your app. It’s essential to ensure that the code is correctly implemented for accurate tracking.
- Test Your Tracking: After implementing the tracking code, perform test conversions to verify that the tracking is working correctly. This step is crucial to ensure that you’re accurately recording user actions.
- Monitor and Adjust: Once Conversion Tracking is set up, regularly monitor the data it provides. Analyze which keywords, ads, and campaigns are driving the most conversions. Use this information to make data-driven decisions and optimize your campaigns accordingly.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid:
- Inaccurate Tracking: Ensure that the tracking code is correctly implemented on all relevant pages of your website. Inaccurate tracking can lead to incorrect data and misguided campaign decisions.
- Misaligned Goals: Make sure your conversion goals align with your business objectives. Tracking the wrong actions can lead to misleading insights.
Interpreting Conversion Data
Once your Conversion Tracking is in place and collecting data, the next crucial step is interpreting that data effectively. Here are some key aspects to consider when analyzing conversion data:
- Attribution Models: Google Ads offers different attribution models that determine how conversions are attributed to various touchpoints in the customer journey. Understanding these models is vital for assessing the impact of your ads throughout the conversion path.
- Conversion Funnel Analysis: Analyze the conversion path users take on your website. Which pages do they visit before converting? Identifying common patterns can help you optimize your website and ad campaigns to facilitate conversions.
- Return on Investment (ROI): Calculate your ROI by comparing the value of conversions (e.g., revenue generated) to the cost of advertising. ROI insights help you determine which campaigns are profitable and which may need adjustments.
- Conversion Rate Optimization (CRO): Use conversion data to optimize your website’s design and user experience. Small changes to landing pages, forms, or checkout processes can have a significant impact on your conversion rate.
Understanding and interpreting conversion data enables you to make informed decisions to improve campaign performance and maximize your ROI. By tracking conversions effectively, you’ll gain valuable insights into what drives success in your Google Ads campaigns.
As we wrap up this chapter, keep in mind that Conversion Tracking is not a set-and-forget process. It requires continuous monitoring and optimization to adapt to changing user behaviour and market dynamics.
Ready to Take Your Google Ads Campaigns to the Next Level?
Mastering CPC, CTR, and Conversion Tracking in Google Ads is your key to success. These numbers help you manage costs, measure ad effectiveness, and find your way to better returns. Remember, success is an ongoing journey, not a one-time goal. Keep watching, testing, and improving your campaigns.
Team up with Ubique Digital Solutions, your digital marketing partner. We’re here to take your business to new heights online. Contact us now to make the most of Google Ads and open doors for your brand. Your success story starts here!
FAQs
Q: What’s a good CTR in Google Ads, and how can I achieve it?
A good CTR (Click-Through Rate) varies by industry but typically ranges from 1% to 5%. To improve it, focus on relevant keywords, compelling ad copy, and well-structured campaigns.
Q: How does Google calculate CPC, and why does it vary for different keywords?
Google calculates CPC (Cost-Per-Click) through an auction system. The price varies because it depends on competition, quality score, and bid amount for each specific keyword.
Q: What are some advanced bidding strategies for CPC optimization?
Advanced bidding strategies include Target CPA, Target ROAS, and Enhanced CPC. These strategies use machine learning to optimize your bids for better results.
Q: How can I track conversions for different goals in Google Ads?
Set up conversion tracking in Google Ads by creating conversion actions for specific goals like website purchases, form submissions, or phone calls. Use the provided code to track these actions on your site.
Q: What tools and resources can help me analyze conversion data effectively?
Google Analytics and Google Tag Manager are useful tools for in-depth conversion data analysis. Additionally, Google Ads reports and third-party analytics software can provide valuable insights.