Understanding the Traditional Funnel
The marketing funnel concept isn’t new, but understanding its origins and evolution can provide crucial insights into how businesses have adapted their strategies to the ever-changing consumer landscape.
1. The Birth of the Funnel Concept
The basic idea behind the marketing funnel dates back to 1898 when E. St. Elmo Lewis developed the AIDA model. AIDA stands for Awareness, Interest, Desire, and Action. Lewis aimed to map out a customer’s journey, from the first time they learn about a product to the moment they purchase it. This structure became the foundation upon which the marketing funnel was built.
2. The Linear Journey
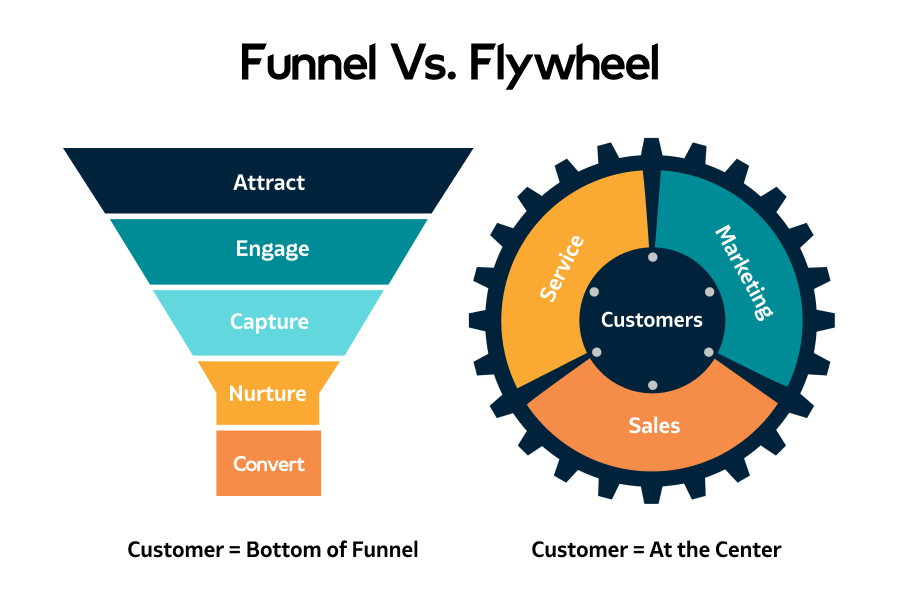
The traditional marketing funnel visualised the customer’s journey as linear, moving them from one stage to the next. It was shaped like a funnel to represent the many people at the awareness stage and the smaller number who eventually take action by making a purchase.
3. Expanding the Concept
Over the years, as their understanding of consumer behaviour deepened, marketers started to add more stages to the funnel. The nuances of evaluation, decision-making, and post-purchase behaviour became important. As a result, models that expanded on the AIDA concept emerged. For instance, some funnels included stages like ‘Consideration’, ‘Preference’, or ‘Loyalty’.
4. Challenges and Criticisms
As businesses evolved and the market became more competitive, it was evident that the linear funnel model had limitations. One major criticism was that it didn’t adequately consider post-purchase stages, like retention, loyalty, and advocacy. The traditional funnel often ended once a sale was made, overlooking the potential of repeat customers or the value they brought in terms of referrals.
5. Adapting to the Digital Age
The customer journey has become more complex with the internet and digital technologies. Now, consumers have multiple touchpoints and channels to engage with brands. This necessitated a more intricate and flexible model than the traditional funnel. Marketers began to look at multi-channel funnels and the concept of ‘micro-moments’ to represent better the modern consumer’s path to purchase.
6. Enter New Models
The perceived shortcomings of the traditional funnel and the changing digital landscape led to the proposal of new models. One such model is the Flywheel, which retains momentum by keeping existing customers engaged and turning them into brand advocates. Unlike the linear funnel, the flywheel model is cyclical, representing a continuous, dynamic customer journey.
Critical Stages of the Traditional Funnel
Awareness
This is when potential customers first become aware of a product or brand. The primary goal here is visibility. Techniques such as search engine optimisation (SEO), pay-per-click advertising, and public relations campaigns can boost a brand’s presence in the market, ensuring it captures the target audience’s attention.
Consideration
Once customers know a brand, they move to the consideration phase, where they weigh their options. During this phase, the role of reviews, testimonials, case studies, and content marketing becomes paramount. These tools provide essential information and build trust, nudging the consumer closer to purchasing.
Conversion
The most critical stage, conversion, is where prospects become customers. Businesses employ targeted offers, compelling call-to-action statements, streamlined website navigation, and efficient checkout processes to enhance conversion rates.
Post-Purchase (Loyalty & Advocacy)
After the sale, the journey doesn’t end— on post-purchase engagement to foster loyalty. Methods like loyalty programs, post-purchase surveys, and effective customer service can ensure that one-time buyers become repeat customers and, eventually, brand advocates.
Diving into the Flywheel Model
What is the Flywheel Model?
The flywheel model is a newer concept inspired by the mechanics of a physical flywheel, which retains momentum and keeps going once spinning. Instead of viewing the customer journey as a linear path, the Flywheel sees it as a continuous cycle: Attract, Engage, and Delight.
Components of the Flywheel
Engage
Engagement is about more than just making a sale. It’s about building and maintaining relationships. This is achieved through personalised marketing, effective communication channels, and fostering a sense of community around the brand.
Delight
Post-purchase, the flywheel model emphasises turning customers into enthusiastic promoters. This is achieved by exceeding expectations, providing exceptional customer service, and leveraging user-generated content to amplify brand advocacy.
Comparing the Two: Which One is More Effective?
Aspect | Traditional Funnel | Flywheel Model |
| Conceptual Structure | Linear model with stages: Awareness, Consideration, Conversion, Post-Purchase (Loyalty & Advocacy) | A cyclical model with steps: Attract, Engage, Delight |
| Customer Journey View | Sequential: Customers progress through stages in a linear manner | Continuous: Customer journey loops back and repeats |
| Customer Focus | Acquisition-focused: Emphasis on attracting new customers | Retention-focused: Focus on customer satisfaction and loyalty |
| Post-Purchase Emphasis | Limited focus on post-purchase engagement | Strong emphasis on post-purchase engagement and advocacy |
| Strengths | – Clear and structured framework for understanding the sales process – Easy to implement and measure progress | – Focus on customer retention and advocacy increases customer lifetime value – Builds sustainable business momentum |
| Weaknesses | – Neglects post-purchase stages and customer retention – Limited visibility on the impact of customer advocacy | – More challenging to measure and quantify the Flywheel’s efficiency – Initial traction may be slow to build momentum |
| Flexibility | It is somewhat rigid, as it follows a linear path | More adaptable to changes in consumer behaviour and market dynamics |
| Suitable for | – Businesses with straightforward and short sales cycles – One-time transactional products or services | – Businesses seeking long-term customer relationships – Repeat purchases and referral-based growth |
Strengths and Weaknesses of the Traditional Funnel
The funnel’s linear funnel has both its strengths and weaknesses. While it provides a clear path from marketing to sales, it often neglects the post-purchase phase, potentially leaving out opportunities for upselling, retention, and advocacy.
Strengths and Weaknesses of the Flywheel Model
The Flywheel’s emphflywheel’s emphflywheel’sntinuous momentum highlights the importance of every customer interaction. Its circular nature values referrals and repeat business, although some companies might find its holistic approach challenging to implement effectively.
The Verdict
Situational Effectiveness
Determining the most effective model between the Traditional Funnel and the Flywheel depends on a business’s unique circumstances and goals. Each model has strengths and weaknesses, making them more suitable for specific situations. Let’s explore the transformational effectiveness of each model:
Traditional Funnel
- Short and Simple Sales Cycles: The traditional funnel is well-suited for businesses with straightforward and short sales cycles. If the decision-making process for your product or service is relatively quick and requires minimal consideration, the funnel can efficiently guide potential customers towards purchasing.
- Transactional Products or Services: The traditional funnel can effectively drive initial conversions for businesses that primarily offer one-time transactional products or services. Customers who don’t require don’t engagement might not benefit as much from the Flywheel’s focal wheel’s purchase stages.
- Lead Generation and Immediate Impact: The linear funnel allows marketers to implement and measure lead generation efforts more efficiently. It also tends to have a more immediate impact on sales than the Flywheel, which may take time to build momentum.
Flywheel Model
- Long-Term Customer Relationships: The Flywheel is ideal for businesses prioritising long-term customer relationships. The Flywheel nurtures customer loyalty and advocacy by focusing on post-purchase stages like engagement and Delight, leading to repeat business and positive referrals.
- Repeat Purchases and Customer Retention: For companies that rely on repeat purchases or subscription-based models, Flywheel’s rete flywheel approach can be more effective. The model’s emphasis on customer satisfaction encourages customer retention and reduces churn.
- Referral-Based Growth: Businesses seeking to harness the power of word-of-mouth marketing and customer advocacy will find the flywheel model advantageous. Satisfied customers turned brand advocates can generate organic growth through referrals.
- Complex and Long Sales Cycles: When the sales process involves multiple touchpoints and a more extended consideration phase, Flywheel cont flywheel’s approach aligns better with the customer journey.
Hybrid Approach
In some cases, a hybrid approach that combines the traditional funnel and Flywheel elements might be the most effective strategy. For example, a business can use the horn to attract and convert new customers and then transition them into the flywheel model to nurture and retain them.
Future Trends and Predictions
The integration of technology, especially AI, is set to revolutionise both models, making personalisation and predictive analytics even more refined. As consumer behaviour evolves, so will the models that map their journeys.
HubSpot Flywheel Model
HubSpot’s Flywheel Model is a customer-centric approach to business growth that replaces the traditional sales funnel concept. It reimagines the way companies attract, engage, and delight customers by focusing on building long-lasting relationships and fostering customer advocacy. The Flywheel Model is designed to align marketing, sales, and customer service efforts to create a self-sustaining cycle of growth.
Here are the key components of the HubSpot Flywheel Model:
- Attract: The first phase of the Flywheel Model involves attracting potential customers to your business. This is accomplished by creating valuable content, optimizing for search engines, leveraging social media, and other inbound marketing tactics. The goal is to bring in visitors and convert them into leads by offering something of value, such as eBooks, webinars, or free trials.
- Engage: Once you have generated leads, the next step is to engage with them effectively. This phase is all about nurturing leads and building meaningful relationships. Marketing automation, email campaigns, personalized content, and targeted messaging are essential tools in this stage. The goal is to turn leads into customers by providing relevant and timely information.
- Delight: After a customer makes a purchase, the relationship doesn’t end. It’s just the beginning. The delight phase is all about exceeding customer expectations, providing exceptional customer service, and creating a positive experience. Happy customers are likelier to become promoters, referring others to your business and providing valuable feedback.
- Feedback Loop: The Flywheel Model emphasizes the importance of collecting feedback from customers at every stage of their journey. This feedback loop helps you better understand their needs, pain points, and preferences. By actively listening to customers, you can improve your products, services, and processes.
Here are some benefits of adopting the HubSpot Flywheel Model:
- Customer-Centric Approach: The Flywheel Model places the customer at the centre of your business strategy, reinforcing the importance of delivering value and exceptional experiences.
- Sustainable Growth: The Flywheel Model promotes long-term, sustainable growth by focusing on customer satisfaction and advocacy. Happy customers are more likely to stick around and refer others.
- Alignment of Teams: The model encourages better alignment between marketing, sales, and customer service teams. When these teams work together cohesively, it creates a smoother customer journey
- Continuous Improvement: The feedback loop inherent in the Flywheel Model ensures that you are continually improving your products and services based on customer insights.
- Reduced Churn: Prioritizing customer delight can lead to lower customer churn rates, reducing the need for constant customer acquisition efforts.
Why Choose HubSpot Partner – Ubique Digital Solutions?
As you evaluate your company’s needs, consider the nature of your product or service, the complexity of your sales cycle, and the importance of customer retention and advocacy. Tailoring a suitable marketing model to fit your specific requirements will enable you to maximise your marketing efforts and drive long-term success.
For expert guidance in implementing the most effective marketing strategy and taking your business to new heights, partner with Ubique Digital Solutions, a platinum HubSpot partner. Our team of skilled professionals is dedicated to providing cutting-edge solutions, innovative marketing techniques, and personalised strategies using HubSpot services that will propel your business forward. Contact us today.
FAQs
Q: How do I transition from a funnel approach to a flywheel model?
Transitioning from a funnel to a flywheel requires a shift in mindset. Focus on customer retention, understand the lifetime value of a customer, and encourage brand advocacy.
Q: Are there businesses for which the traditional funnel still makes more sense?
The traditional funnel might be more applicable for businesses with one-off products or services and a straightforward, linear customer journey.
Q: How do technological advancements (like AI) influence these models?
AI can enhance personalisation, predict consumer behaviour, and automate tasks, benefiting both models and potentially revolutionising the Flywheel with predictive engagement strategies.
Q: Can both models be integrated into a hybrid approach?
Absolutely! A hybrid approach can combine the funnel’s claritfunnel’s flywheel’s momeflywheel, maximising both strengths.
Q: How does the customer retention feature in the Flywheel compare to the traditional funnel?
While the traditional funnel often ends post-purchase, the Flywheel places significant emphasis on post-purchase engagement and retention, making customer retention central to its strategy.